A cloud security strategy is an established set of tools, rules, and procedures for safeguarding cloud data, apps, and infrastructure against security threats. It covers encryption, identity and access management, network segmentation, and intrusion detection systems. The cloud security plan deals with your unique business security concerns while aligning with your overall security goals, including continuous threat monitoring and response methods.
Understanding the Basics of Cloud Security Strategy
Knowing the cloud service types, OSI model layers, shared responsibility, deployment models, and DevSecOps will help you create a more effective cloud security strategy. It improves your company’s threat response and enables you to apply best practices more efficiently. Mastering these areas ensures a comprehensive and adaptable approach to cloud security.
Cloud Service Types
Cloud security delivers a variety of service options to meet different company demands. These cloud service models are broadly classified into three types: infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS), platform-as-a-service (PaaS), and software-as-a-service (SaaS). Each of these models offers the customer various levels of control and responsibility.
- IaaS: Uses virtualized computing resources online, allowing users to manage operating systems, storage, and applications while the vendor handles hardware and networking.
- PaaS: Creates a platform enabling clients to design, run, and manage apps using vendor tools without having to manage the underlying infrastructure and middleware.
- SaaS: Includes ready-to-use software applications via the internet, controlled entirely by the vendor, with little customer configuration and maintenance requirements.
The OSI Model
The OSI Model’s layers help develop a safe cloud environment. Understanding the relationship between the OSI Model Layers and your cloud security strategy allows you to simplify intricate security concepts, make more informed security decisions, and boost collaboration and interaction. Effective cloud security is established layer by layer. The following describes how each layer of the OSI Model relates to cloud security:
- Physical layer: Enables physical protection for data centers, guarding against unwanted access and physical harm.
- Data link layer: Uses VLANs and MAC filtering to regulate access and ensure secure communication between nodes.
- Network layer: Protects data in transit and ensures safe network paths by utilizing firewalls, VPNs, and secure routing protocols.
- Transport layer: Employs SSL/TLS to ensure data integrity and confidentiality during transmission.
- Session layer: Manages secure sessions by utilizing authentication protocols and session management mechanisms to prevent unauthorized access.
- Presentation layer: Utilizes encryption and data formatting standards to ensure data confidentiality and integrity throughout processing and storage.
- Application layer: Includes app-level security features such as API, web application firewalls (WAFs), and endpoint protection to protect user interactions and app data.
The Shared Responsibility Model
The shared responsibility model assigns cloud security tasks to both the vendor and the customer. Customers safeguard data, applications, and configurations; providers secure the infrastructure. Understanding this division of responsibility results in good cloud security management, ensuring each party implements appropriate measures to reduce risks.
Cloud Deployment Models
Understanding the many types of cloud environments enables you to choose the appropriate deployment option for your organization’s needs. Here are the five main cloud deployment models:
- Public cloud: Managed by third-party companies that provide services over the internet with multi-tenancy, in which clients share server space with other enterprises.
- Private cloud: Utilized by a single business and can be hosted on-premises or in a provider’s data center, ensuring internal multi-tenancy.
- Hybrid cloud: Combines several cloud instances (public or private) with portability, typically provided by solutions such as Microsoft’s Azure Stack or VMware on AWS.
- Multi-cloud: Uses many public and private clouds simultaneously, distributing apps and data across multiple providers.
- Multi-tenant cloud: A public cloud architecture feature that allows multiple clients to share the same environment while keeping their data segregated.
Explore how to protect your cloud deployment by reading our guide on how to secure the five cloud environment types, the risks, and prevention methods.
DevSecOps
Integrating security into the SDLC is fundamental to cloud resilience. DevSecOps integrates security into development, deployment, and operations, proactively finding vulnerabilities. DevSecOps supports collaboration by bringing together development, operations, and security teams, resulting in secure, dependable systems delivered at modern business speeds. This strategy addresses cloud security needs by building a comprehensive, adaptive security culture.
Why Is Cloud Security Strategy Important?
Any business that wants to benefit from cloud computing while keeping its data safe and secure needs a secure cloud strategy. Organizations can defend their assets and maintain consumer trust by addressing cyber risks, obtaining a competitive edge, assuring full-stack visibility, adopting proactive security, and allowing business agility.
- Mitigates cyber threats: Implements strong security procedures to prevent data breaches, income loss, and reputational damage. Protects sensitive data against unauthorized access.
- Gains a competitive advantage: Emphasizes data protection methods integrated into a well-designed cloud security strategy to foster client trust and sets it apart from the competition.
- Ensures full-stack visibility: Provides complete visibility across your cloud infrastructure, allowing you to identify and solve security concerns. Detects anomalies and responds quickly, with a comprehensive view of all resources.
- Adopts proactive security: Uses automated technologies for vulnerability scans and misconfiguration checks to identify and address threats before they arise. Prevents mishaps and reduces the severity of threats.
- Enables corporate agility: Integrates new cloud services and scales security operations to meet changing business needs. Maintain flexibility in your security plan to meet the changing business needs.
Core Components of a Robust Cloud Security Strategy
To properly secure your cloud environment, prioritize five key cloud security strategy components: visibility, exposure management, prevention, detection, and response. Focusing on these components allows organizations to develop a comprehensive and successful cloud security strategy to protect their assets and operations.
- Visibility: Maintain complete insight into your cloud architecture to effectively manage and secure dynamic resources. Without visibility, you risk being exposed to security risks since you can’t protect what you can’t see.
- Exposure management: Reduce risk by resolving vulnerabilities and coordinating the IT and security teams. Effective exposure management necessitates teamwork to prioritize and reduce risks that may interrupt corporate operations.
- Prevention controls: Implement security controls that are specifically designed for cloud environments. As you adapt to the cloud, ensure that existing tools are compatible and that controls are updated to handle new attack vectors and emerging risks.
- Detection: Quickly detect security breaches to limit their damage. Given the scarcity of cybersecurity experts, use automated systems or third-party services to monitor and detect irregularities in your environment constantly.
- Response: Create and maintain a documented response plan that specifies roles, responsibilities, and processes for handling breaches. Regularly test, review, and update this strategy to ensure it’s ready for successful event management and recovery.
7 Steps in Building a Robust Cloud Security Strategy (+ Template)
Creating a strong cloud security strategy requires an integrated strategy that includes reviewing your current environment, assessing costs, establishing security objectives, designing your architecture, creating policies, implementing solutions, and conducting ongoing testing. This takes care of your organization’s data and apps as you transition to and operate in the cloud.
To guarantee that your strategy remains effective, it must be dynamic and adaptable to new services, features, and threats. Here’s a systematic way to develop and sustain a complete cloud security plan.
Assess Your Current Cloud Environment
Begin by assessing the condition of your IT ecosystem. Identify inefficiencies and create a baseline for comparison with the existing infrastructure. Determine which applications are appropriate for cloud transfer. Consider storage capacity, data type, network environment, and analytics applications. This study will help inform migration decisions and plan creation.
Evaluate Costs & Resources
Assess the costs and resources involved with your current IT infrastructure. Examine the associated expenses of physical servers, maintenance, and manpower. Compare these expenditures against the potential savings and efficiencies from cloud migration. Your assessment helps your business justify the transition to the cloud and shows potential productivity and cost-effectiveness gains.
Define Security Objectives & Requirements
Set specific security goals and standards depending on your organization’s needs and regulatory constraints. Define what you want to protect, the level of security required, and the compliance standards to achieve. This stage ensures that your security plan is aligned with company objectives and meets specific security requirements.
Design Your Cloud Security Architecture
Build a security architecture for your cloud environment. Consider network security, data protection, identity management, and access controls during the design process. A well-structured architecture serves as a solid platform for applying security measures and efficiently protecting your cloud resources.
Develop Security Policies & Procedures
Create comprehensive security policies and procedures to help guide your cloud operations. Include policies on data security, incident response, access management, and compliance. Clear policies guarantee that security techniques are used consistently and help to manage risks methodically.
Implement Security Measures
Implement the security measures outlined in your strategy. This includes deploying technologies for encryption, monitoring, vulnerability management, and threat detection. Implementing these procedures secures your cloud environment against potential attacks and weaknesses.
Test & Refine Your Strategy
To guarantee that your cloud security plan is effective, review and improve it regularly. Conduct vulnerability assessments, penetration testing, and simulated security incidents. Use the data to continually upgrade and enhance your security posture to respond to new threats and changes in your cloud environment.
Cloud Security Strategy Template
This downloadable template will assist your business in developing a customized cloud security strategy to meet your specific requirements. Use the document as a full or partial guidance to create your own approach. Click the image below to download and modify your copy.
Common Cloud Security Strategy Vulnerabilities
Vulnerabilities such as data breaches, misconfigurations, insider threats, and DDoS attacks all weaken the effectiveness of your cloud security approach. Organizations can reduce these risks and improve their cloud security posture by implementing preventive measures such as strong access controls, automated configuration management, effective IAM policies, and DDoS protection.
Data breaches
Data breaches occur through various means, including cyberattacks, insider threats, or weaknesses in cloud services. Attackers may exploit vulnerabilities to access confidential information, resulting in unauthorized disclosure.
To mitigate data breaches, use robust access controls, encryption, and continual monitoring. Regularly update security processes and conduct vulnerability assessments to detect and remedy potential flaws before they’re exploited.
Misconfigurations
Misconfigurations happen when cloud resources or services aren’t correctly configured, which is generally due to human mistakes or a lack of knowledge. This can expose data unintentionally and pose security issues.
To avoid misconfigurations, use automated tools to detect and rectify mistakes. Establish and enforce configuration management standards, and encourage employees to follow the best practices for cloud setup and maintenance.
Insider Threats
Insider threats refer to unlawful or careless actions by workers or contractors who have access to cloud systems and data. These individuals may purposefully or unintentionally cause data breaches or other security vulnerabilities.
To reduce insider threats, establish strong identity and access management (IAM) policies, such as least privilege access and regular access reviews. Educate personnel about security practices and keep an eye out for unusual conduct.
DDoS Attacks
Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks flood cloud services with traffic, making them inaccessible to authorized users. Attackers employ botnets to flood resources, creating service outages.
Reduce DDoS attacks by implementing DDoS defense technologies and traffic filtering mechanisms. Work with cloud service providers that provide DDoS mitigation services, and design your architecture to withstand high traffic volumes and attacks.
Explore our guide on the top cloud security issues and recognize the differences in cloud threats, risks, and challenges. Learn how to properly prevent each risk to improve your cloud security approach.
Common Challenges & Pitfalls in Building a Cloud Security Strategy
Creating an effective cloud security strategy involves many challenges, including a lack of visibility, misconfigurations, and human error, compliance issues, shared responsibility model issues, complicated cloud environments, and adapting to continuously evolving cloud tools. Address these issues with effective tools and techniques to develop a strong cloud security plan that adapts to the changing cloud landscape while protecting your assets.
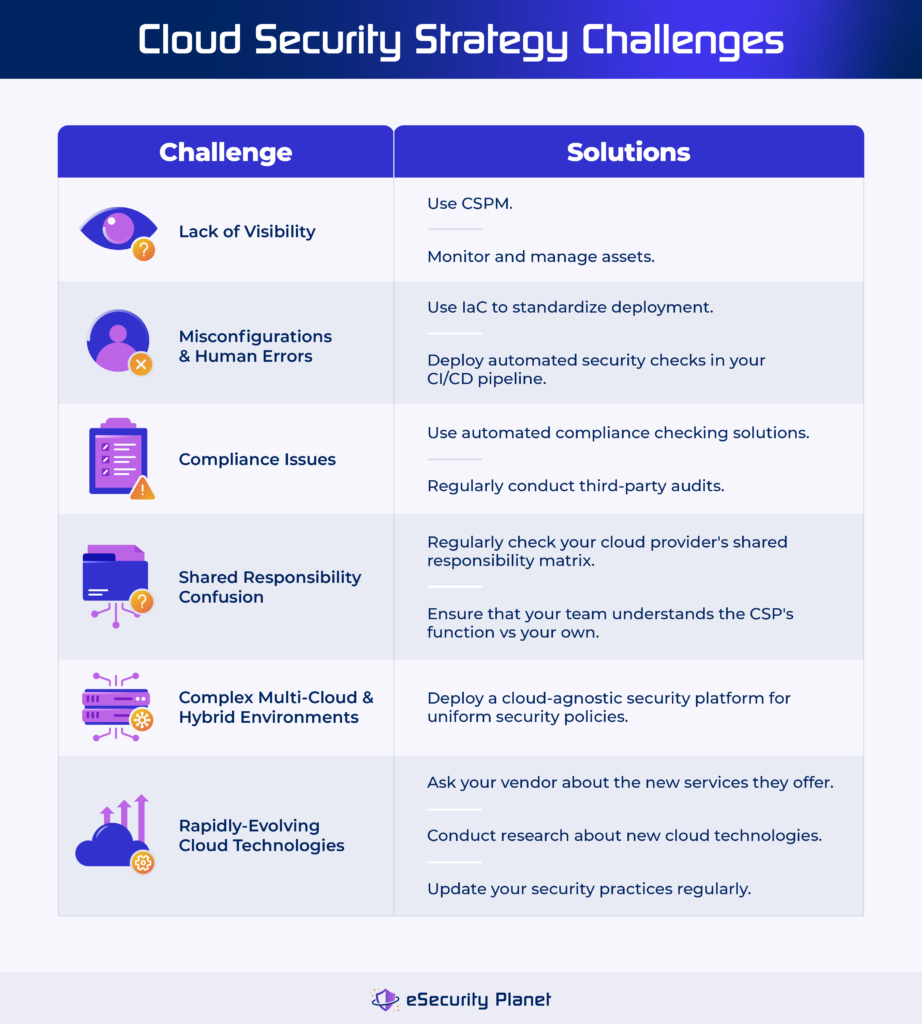
Lack of Visibility
Enterprises moving to the cloud frequently lose complete visibility over their assets. This can lead to vulnerable endpoints, misconfigured resources, and shadow IT concerns where staff use unauthorized applications.
Solution: Use cloud security posture management (CSPM) tools to acquire visibility into your cloud environment. By properly monitoring and managing cloud assets, these technologies aid in identifying security concerns and the overall security of the cloud.
Misconfigurations & Human Errors
The level of complexity and speed of cloud provisioning can lead to setup errors, which attackers frequently exploit. Human errors during setup might also lead to security vulnerabilities.
Solution: Use infrastructure-as-code (IaC) to standardize and automate deployment. Implement automated security checks in your CI/CD pipeline to detect and remediate misconfigurations before going live.
Compliance with Regulatory Standards
Adhering to multiple laws and regulations can be difficult, especially given the dynamic nature of cloud infrastructures. Keeping up with compliance regulations across several areas and industries can be difficult.
Solution: Employ automated compliance checking solutions that are adapted to individual regulatory requirements. Conduct third-party audits regularly to verify that compliance assessments are objective and complete.
Shared Responsibility Model Confusion
The shared responsibility model allocates security responsibilities to the cloud provider and the customer. Misunderstanding this distinction might result in gaps in security coverage, leaving crucial areas vulnerable.
Solution: Refer to your cloud provider’s shared responsibility matrix regularly to understand your security duties. To properly cover all aspects of security, ensure that your staff understands the provider’s function in relation to your own.
Complex Multi-Cloud & Hybrid Environments
Managing numerous cloud providers or mixing on-premises and cloud solutions can result in inconsistencies in security postures, making it difficult to enforce consistent security standards.
Solution: Deploy a cloud-agnostic security platform to establish uniform security policies across many environments. This technique ensures consistent protection and simplifies security management across various cloud and hybrid deployments.
Rapidly-Evolving Cloud Technologies
The quick expansion of cloud services brings new features and potential problems. Staying ahead of these changes ensures a secure cloud strategy.
Solution: Ask your existing vendor or research cloud security technologies to discover new services and the potential risks they introduce. To handle emerging risks and remain proactive, update your security practices regularly.
9 Cloud Security Strategy Best Practices
Implementing effective cloud security strategies and best practices protects your data and apps in the cloud. Understanding your environment, getting visibility, recognizing risks, adhering to governance frameworks, and implementing multi-layer security solutions will help you effectively secure your data and applications from potential threats.
Understand Your Cloud Environment
Before developing a security strategy, thoroughly understand your cloud environment. To effectively design your security measures, identify the types of data and applications you hold and the associated risks and vulnerabilities.
Gain Full Cloud Visibility
Gain complete access to your cloud infrastructure. Ensure 100% visibility across all cloud architectures, including team-specific normalization and segmentation. Implement features like RBAC, full inventory, automated detection, and configuration visibility. Automated, continuous visibility allows you to monitor the proportion of your surroundings.
Identify & Remediate Critical Cloud Risks
Understand workload and cloud risks, identify attack vectors, and prioritize essential concerns. Implement cloud tool features such as exposure analysis, misconfiguration, and vulnerability management, secure secret storage, and attack route analysis. Monitor the number of open critical issues and assess overall decreases over time.
Recognize the Common Cloud Threats
Identify internal and external threats in your cloud environment. This includes malicious insiders, hackers, and cybercriminals. Use threat intelligence to remain on top of prospective threats and adjust your security posture accordingly.
Establish a Cloud Governance Framework
Create a cloud governance framework to oversee data security, system integration, and cloud deployment. This provides risk management, data protection, and conformity to regulatory requirements. Regularly update your governance policies to reflect changing compliance requirements.
Employ a “Shift Left” Approach
Implement security protections early in the application development lifecycle using a “shift left” technique. Integrate pre-production security testing, vulnerability scanning, and compliance assessments directly into CI/CD pipelines to anticipate and resolve issues.
Implement Multi-Layer Security
Use a multi-layered security technique to protect your cloud environment. To ensure complete network and data security, deploy firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention systems, and security information and event management (SIEM) tools.
Encrypt Your Data
Utilize encryption tools to protect sensitive data in the cloud. Ensure that data is encrypted both in transit and at rest. Make it a necessary part of your security strategy to prevent unauthorized access.
Monitor & Audit Your Infrastructure
Perform regular monitoring and auditing of your cloud infrastructure. To discover and respond to security problems quickly, review logs and security alerts, and conduct frequent vulnerability assessments.
Integrate the best practices above with the general cloud security best practices to achieve an enhanced cloud protection.
Case Studies & Real-World Examples
Real-world cloud incidents, such as Toyota’s data breach, Atlassian Jira’s database issues, and Microsoft outages, highlight the crucial need for strong security measures. These situations demonstrate how gaps in cloud security can cause severe disruptions.
According to the Cybersecurity Insiders 2023 cloud report, 95% of security experts are deeply concerned about public cloud security. This emphasizes the importance of continual education, adaptable solutions, and effective techniques for addressing underappreciated hazards. To strengthen cloud security, install comprehensive protection measures, invest in ongoing training, and modify your strategies to reduce risks and the impact of interruptions.
Toyota Exposed 260,000 Customer Data in 2023
Toyota faced a breach in June 2023 due to a misconfigured cloud environment, which exposed data from 260,000 customers. The intrusion went undiscovered for several years, exposing sensitive information like in-vehicle device IDs and map data updates.
How a secure cloud strategy could help:
- Configuration management: Use IaC and automated configuration management to avoid misconfiguration. Review and update configuration settings regularly.
- Continuous monitoring: Employ CSPM tools to constantly monitor configurations and discover anomalies that may signal a misconfiguration.
- Incident detection and response: Implement effective incident detection techniques to detect breaches early and shorten exposure time.
Database Upgrade Affects Atlassian Jira
Atlassian’s Jira project management platform experienced failure and downtime in January 2024 due to issues related to a scheduled database upgrade. This affected many Jira services, causing them to be unavailable for almost four hours.
How a secure cloud strategy could help:
- Change management: Include extensive testing and validation of modifications prior to deployment. Make sure your backup and rollback protocols are in place.
- Disaster recovery: Create and test a disaster recovery strategy regularly to ensure that services are restored, and redundancy and failover solutions are in place.
- Performance monitoring: Use performance monitoring technologies to identify and resolve issues before they affect end users.
A Series of Microsoft Outages in 2024
In July 2024, Microsoft had massive outages affecting various Azure services and Microsoft 365. On July 13, a configuration update in Azure’s OpenAI service caused problems owing to the elimination of unused resources, affecting both storage and compute resources. This problem was followed by more outages on July 18-19, which impacted connection and service management operations in the Central US region.
Additionally, the issue caused disruptions to Microsoft’s status page and other services. These disruptions were heightened by a faulty CrowdStrike update, which created confusion about the root cause.
How a secure cloud strategy could help:
- Configuration management: Set up a robust configuration management strategy to handle updates and changes methodically. Use automated tools to validate configuration changes before they go live.
- Resilience and redundancy: Include redundancy in cloud architecture to maintain service continuity during outages. Use multi-region deployments to alleviate the effects of regional difficulties.
- Incident communication: Maintain clear communication lines with users during outages. Provide timely status updates to all affected users, including all the mitigation actions your team performed.
- Redundancy and failover planning: Develop a strategy that includes redundancy and failover measures to reduce the effect of failures by maintaining continuous service availability and automated traffic rerouting.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What Is a Cloud-First Strategy?
A cloud-first approach prioritizes cloud-based solutions above on-premises infrastructure. Organizations choose to use external cloud services rather than build and manage their own technology infrastructure. This method uses the provider’s infrastructure to provide efficient, high-quality services, promoting scalability, flexibility, and lower maintenance costs than in-house operations.
What Are the 4cs of Cloud-Native Security?
The four Cs of cloud-native security — code, container, cluster, and cloud — comprise a layered security strategy. Code security entails protecting application code and APIs. Container security focuses on safeguarding container runtimes such as Docker and Kubernetes. Cluster security focuses on the infrastructure that runs containers. Cloud security ensures that the underlying cloud infrastructure is secure.
What Are the 5 Pillars of Cloud Security?
Cloud security is built on five pillars: identity and access management (IAM), data encryption, network security, compliance and governance, and incident response and recovery.
- IAM: Manages user access to cloud resources by enforcing the least privilege principle through authentication and authorization, and constant monitoring for suspicious activity.
- Data encryption: Encrypts data at rest and in transit, including end-to-end encryption, and uses secure key management to keep data unreadable to unauthorized users.
- Network security: Uses firewalls, Virtual Private Clouds (VPCs), network segmentation, and security groups to prevent unauthorized access and regulate traffic.
- Compliance and governance: Ensures compliance with regulatory requirements and industry standards by using audit trails, compliance frameworks, and automated checks.
- Security incident response and recovery: Manages security incidents using detection tools, response plans, communication protocols, recovery methods, and post-analysis.
Bottom Line: Enhance Protection with a Secure Cloud Strategy
A cloud security strategy ensures that businesses continue to operate regardless of outages. However, it only provides one layer of protection. Integrate cloud protection with existing network security measures, identify potential risks, and use the appropriate technologies. This comprehensive method offers strong disruption defense, protecting both your cloud environment and your entire network.
Discover how to protect your organization with this comprehensive guide to cloud security fundamentals. Learn about data protection, regulatory compliance, and access control to effectively address challenges and apply best practices.
